PFD Meaning: A Comprehensive Guide to Personal Flotation Devices
PFD is an acronym that holds different meanings in various contexts. It is essential to understand the specific meaning of PFD when encountering it in different fields or industries. One of the most common interpretations of PFD is "Personal Flotation Device," which refers to a life jacket or buoyancy aid designed to keep an individual afloat in water.

Another common meaning of PFD is found in the field of electronics, where it stands for "Power Factor Display," a tool that measures the efficiency of power utilization in electrical systems. PFD can also refer to the "Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend," a fund established to distribute earnings from the state's mineral resources in the United States. In engineering, it is often used as an abbreviation for "Process Flow Diagram," a graphic representation of a process within chemical and process engineering.
Key Takeaways
- PFD holds various meanings in different contexts, such as Personal Flotation Device in water safety
- In electronics, PFD refers to Power Factor Display, while in engineering, it stands for Process Flow Diagram
- The Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend is another instance where the acronym PFD is utilized

Pfd as Personal Flotation Device
A personal flotation device (PFD) is a crucial piece of safety equipment designed to provide buoyancy and help individuals stay afloat in water. These devices play a vital role in preventing drowning incidents and are essential for various water-related recreational activities such as kayaking, canoeing, and stand-up paddleboarding 1.
PFDs come in different types and sizes to accommodate a wide range of users and situations. The United States Coast Guard (USCG) certifies and regulates PFDs, dividing them into five different categories 2. Each type caters to specific needs and conditions for users, ensuring optimal safety and functionality.

The materials used in PFDs contribute significantly to their effectiveness. They often contain foam, air, or a combination of both, providing the necessary buoyancy for people to stay afloat. Some PFDs are designed as vests, while others resemble suits or belts 3.
Using a PFD is not limited to expert swimmers or those engaged in water sports – it is important for everyone who participates in activities near or on the water. Wearing a properly sized life jacket is crucial, as more than two-thirds of all boating fatalities are drowning incidents, and approximately 90% of drowning victims were not wearing a life jacket 4.
While PFDs provide an essential layer of protection and safety in and around water, it is crucial to choose the right type and size for every individual user. This ensures optimal effectiveness, ultimately minimizing the risk of drowning and giving individuals the confidence to enjoy water-related activities.

Pfd in Electronics
PFD in electronics stands for Phase Frequency Detector. It is a crucial component in various electronic devices and communication systems, as it accurately measures the phase difference between two input signals. By determining this difference, designers can effectively control and synchronize circuits in communication systems and other high-performance applications.
A Phase Frequency Detector (PFD) is an essential part of a phase-locked loop (PLL) system. PLL is a control system that produces an output signal with a specific phase relationship to an input signal. It is widely used in radio frequency and telecommunications systems for signal generation, modulation, and synchronization. PFDs play a vital role in maintaining this relationship between input and output signals by identifying phase shifts and correcting the output accordingly.
In addition to phase frequency detectors, the term PFD in electronics can also refer to other components, such as programmable frequency dividers and passive frequency doublers. Programmable Frequency Dividers are used for dividing the input frequency by a specific integer factor to generate a desired output frequency. Passive Frequency Doublers, on the other hand, are devices that double the input frequency through non-linear electronic methods.
To sum up, PFD in electronics generally refers to phase frequency detectors, which are essential components in maintaining synchronicity in communication systems and other high-performance applications. Although it can also relate to other frequency related components like programmable frequency dividers and passive frequency doublers, its primary purpose is to measure and control the phase difference between input signals. By utilizing this essential PFD function, electronic designers can accurately manage and synchronize various devices and systems in the field of technology.

PFD and Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend
The Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend (PFD) is a unique government program in which eligible Alaskan residents receive an annual payment from the Alaska Permanent Fund. Established in 1976, the fund accumulates investment earnings from the state's mineral royalties, primarily from oil and gas production. The main purpose of the PFD is to ensure that all eligible Alaskans benefit from the state's natural resources.
The payout of the PFD is calculated based on a 5-year average of the fund's total earnings, which varies each year. The amount paid to each recipient depends on the fund's performance, with the highest payment recorded at $2,072 in 2015. PFD payments are distributed every year, typically in October, to all eligible residents who have lived in Alaska for at least a full calendar year (from January 1 to December 31).
Eligibility requirements for the PFD include being a resident of Alaska for a full calendar year, physically residing in the state, and intending to remain indefinitely. Certain absence guidelines are in place for potential exceptions, such as military service, education, medical treatment, and more. The PFD applicants must also not have been sentenced or incarcerated due to a felony or misdemeanor conviction during the qualifying year.
The Alaska Department of Revenue's Permanent Fund Dividend Division is responsible for administering the PFD program, ensuring that all eligible Alaskans receive their annual dividend in a timely manner. The division is also responsible for detecting and prosecuting any fraudulent claims, ensuring the program functions fairly for all residents.
As a result of the PFD, Alaska remains the only state in the United States to provide its residents with a direct share of its natural resource wealth. The program stands as a symbol of responsible resource management, stimulating the local economy and fostering a greater sense of ownership and stewardship among Alaskans.
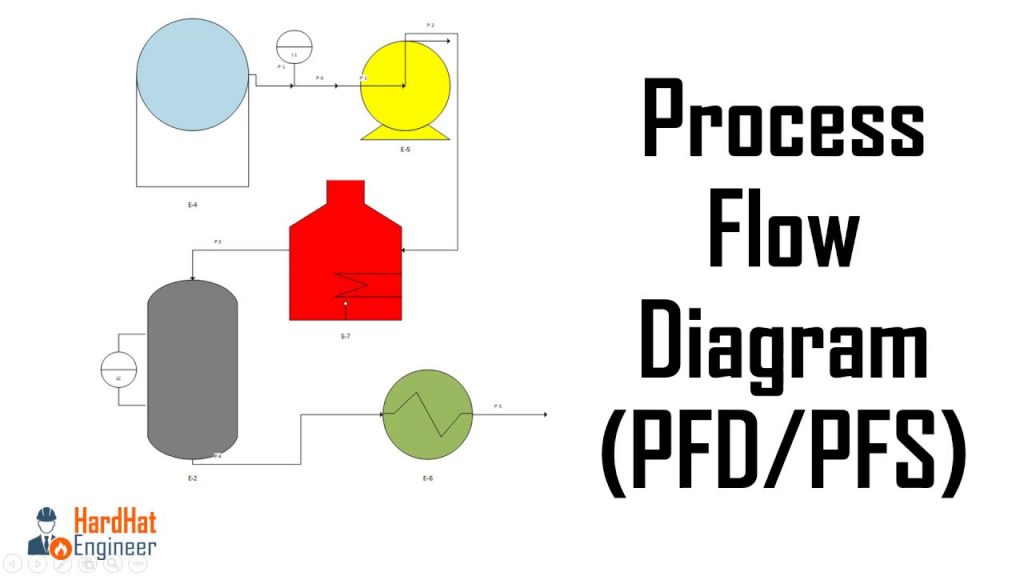
PFD in Engineering
A Process Flow Diagram (PFD) is an essential tool in engineering, particularly in chemical and process engineering. It represents the general flow of plant processes and equipment, providing a quick overview of an operating unit or system 1. By illustrating the relationship between major equipment within a plant facility, a PFD gives engineers and technicians a basis to trace the flow of materials through the unit, making it a core document for drawing Plot Plants and P&IDs 2.
In engineering, PFDs are widely used to communicate critical information about plant operations. They help engineers in understanding the process flow design and making decisions regarding equipment installation, maintenance, and safety procedures. Moreover, PFDs play an essential role in training new employees and providing information to visitors 3.
The PFD displays several entities, such as main equipment, heat, material, and energy balance. It also contains tag numbers and chemical compositions. However, it does not show minor details like piping details and designations 4.
To create an effective PFD, engineers use various symbols and conventions to represent different equipment and processes. For instance, pumps, valves, vessels, and heat exchangers have their standardized symbols. By following these conventions, engineers enable clear communication of the design concepts across different teams 5.
In conclusion, the Process Flow Diagram is an integral part of engineering. It simplifies complex processes and serves as a valuable tool for analysis, communication, and training purposes. By understanding and utilizing PFDs, engineers can ensure efficient operations and a well-organized plant design.

PFD in Medical Context
In medical terms, PFD can represent several meanings. One of the significant interpretations of PFD is Pelvic Floor Dysfunction. Pelvic Floor Dysfunction (PFD) is a collective term that refers to a group of disorders affecting the pelvic floor muscles. These muscles support the bladder, bowel, and uterus in women, or the bladder and bowel in men.
PFD occurs when these muscles become weakened, overly tight, or uncoordinated, resulting in problems related to bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and pain. Symptoms may include urinary and fecal incontinence, constipation, general discomfort in the pelvic region, and painful intercourse. Contributing factors to PFD can be pregnancy, childbirth, surgery, aging, or muscular strain.
Diagnosis for PFD often involves a comprehensive evaluation of medical history, symptoms, physical examination, and, in some cases, specialized tests. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the dysfunction and may include a combination of physical therapy, medication, biofeedback, and, in more severe cases, surgical intervention.
Another meaning for PFD in the medical context is Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia—a rare, non-hereditary bone disorder that occurs when normal bone is replaced with fibrous tissue, leading to weakened bones and deformities. This condition can affect one or multiple bones simultaneously and may result in pain, fractures, and bone deformities. Treatment for Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia focuses on addressing symptoms, preventing complications, and optimizing quality of life.
In summary, PFD can have different meanings in medical contexts, such as Pelvic Floor Dysfunction and Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia. Understanding these conditions helps healthcare professionals in providing accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and better overall patient care.
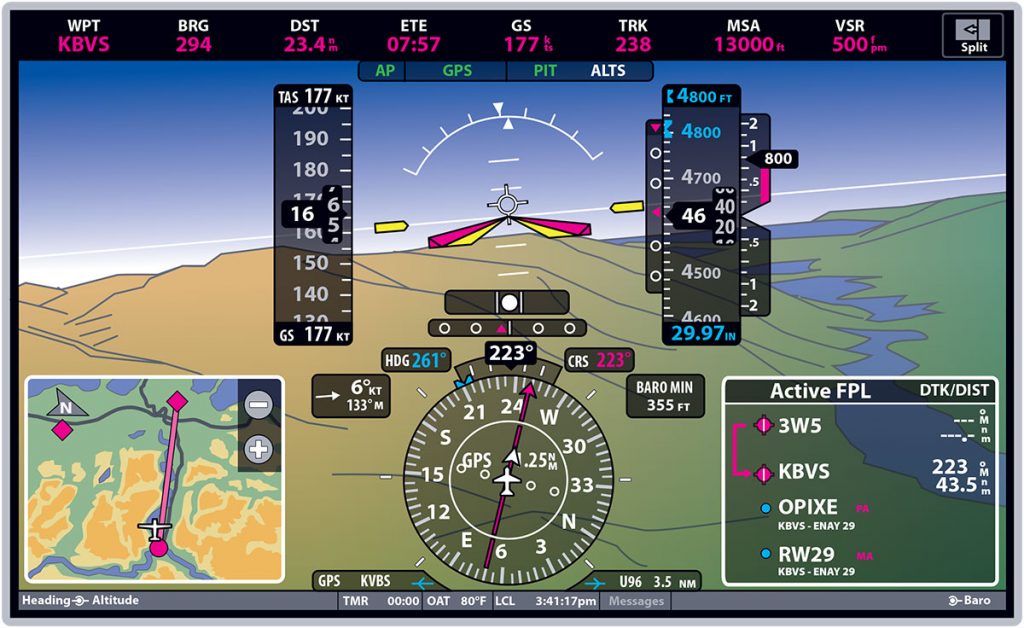
Pfd in Aviation
A Primary Flight Display (PFD) is a crucial piece of technology utilized in modern aviation. Designed to provide pilots with essential flight information, PFDs enhance the overall performance and safety of aircraft operations. By incorporating critical flight data into a single, easy-to-read screen, PFDs enable precise and efficient navigation during flights.
The PFD is a central component of the Electronic Flight Instrument System (EFIS) found in today's advanced aircraft. It offers a digital representation of the traditional analog instruments, consolidating information such as altitude, airspeed, attitude, and navigation into one electronic display. The PFD is typically built around a Liquid-crystal display (LCD) or a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) display device.
The key advantage of a PFD lies in its ability to present comprehensive flight information in a clear, concise format. Pilots can quickly assess their aircraft's status and make informed decisions, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient flight operations. Moreover, the PFD's digital nature allows it to incorporate additional advanced features such as synthetic vision, navigation map displays, and traffic collision avoidance information.
In the realm of aviation, the implementation of PFD technology is quite widespread. From general aviation aircraft to commercial airliners, PFDs have become indispensable tools for pilots to effectively manage their flights. As aircraft technology continues to evolve, enhancements in PFD design and functionality can be expected to further revolutionize the way aviators navigate the skies.

Other Interpretations of Pfd
In addition to the commonly known meaning of Pfd as a "personal flotation device," there are several other interpretations of the acronym, which can be related to various fields and industries.
In the textile industry, Pfd is an abbreviation for "prepared for dyeing." It refers to fabric that has been treated and is ready for the dyeing process. Similarly, in radio and telecommunications, Pfd stands for "power flux density," a measure of the power per unit area received from a radio signal.
In safety and reliability engineering, the term "probability of failure on demand" is referred to as Pfd. This concept is used in the evaluation of safety instrumented systems and is a measure of the likelihood of a system failing to perform its intended function when required.
In legal and administrative settings, a "proposal for decision" is often abbreviated as Pfd. It is a document submitted by an administrative law judge or a hearing officer, outlining their recommendations in a contested case.
Prairie Farms Dairy, a cooperative of dairy farmers from the United States, is sometimes referred to as Pfd. They produce a variety of dairy products, including milk, cheese, and ice cream.
In the scientific domain, the acronym Pfd could stand for "perfluorodecalin," a fluorocarbon compound used as an oxygen carrier in various medical applications. Similarly, a prion-forming domain, or Pfd, in molecular biology, refers to a specific section in a protein sequence that facilitates the formation of prion particles.
There are also several organizations and divisions that use Pfd as an abbreviation. For example, a "public facilities district" is a public corporation or quasi-governmental organization in the United States that provides funding for the development of public facilities. Another example is a "program for faculty development," which is an initiative focused on training and support for educators to enhance their teaching skills. Lastly, the term Pfd can also stand for "policy formulation division," a unit in government or non-government organizations responsible for shaping policies and strategies.
In summary, while Pfd commonly refers to a personal flotation device, it also has a range of meanings across different contexts and industries, showcasing its versatility as an acronym.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does PFD stand for in engineering?
PFD stands for Process Flow Diagram in engineering terms. It is a graphical representation of the flow of a process, and it shows the relationship between the major equipment and components within a process system.
How does a PFD differ from a P&ID?
While both PFD (Process Flow Diagram) and P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram) are used to represent process systems, they serve different purposes. A PFD focuses on the process flow, equipment, and major components, whereas a P&ID provides detailed information on the piping, instrumentation, control systems, and other components involved in the process.
What are the different types of PFDs used in industries?
There are various types of PFDs used in different industries, depending on the specific processes and components involved. Some common types include block flow diagrams (BFDs), which provide a simple overview of the process; process flow diagrams (PFDs), which contain more detailed information on the process steps and equipment; and system flow diagrams (SFDs), which include additional details on the flow of utilities and auxiliary systems.
What is the purpose of a PFD in process design?
The primary purpose of a PFD in process design is to provide a visual representation of the process flow and equipment, allowing for better understanding, communication, and optimization of the system. PFDs help engineers and other stakeholders to gain insights into the process, identify potential issues, and develop strategies for improving the efficiency, safety, and productivity of the process.
How do PFDs help in understanding manufacturing processes?
PFDs help in understanding manufacturing processes by providing a clear and concise representation of the process flow and equipment. They allow stakeholders to visualize the steps involved in the process, the relationships between various components, and the flow of materials and energy throughout the system. This understanding can facilitate more effective communication, troubleshooting, and decision-making related to the process.
What are PFD applications in various fields?
PFDs are used in various fields, including chemical, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, water treatment, and power generation industries. They are essential tools for process design, analysis, optimization, and troubleshooting, as well as for communication between different stakeholders involved in the process. Additionally, PFDs can be used for training, documentation, and regulatory compliance purposes.
Footnotes
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Process_flow_diagram ↩
- https://hardhatengineer.com/what-process-flow-diagram-read-pfd/ ↩
- https://whatispiping.com/process-flow-diagram-pfd/ ↩
- https://processdesign.mccormick.northwestern.edu/index.php/Process_flow_diagram ↩
- https://www.zenflowchart.com/guides/process-flow-diagram ↩
Charlie is Editor-in-Chief of Sea Magazine